Hotline: 4008816860
Hotline: 4008816860
According to the standard, "screw" is a common term, and anything with external threads can be referred to as "screw". The appearance of "nut" is usually hexagonal, with internal holes with internal threads, used to fit with bolts and tighten related components. The head of a "bolt" is usually hexagonal, and the rod has external threads.A thread is a shape with uniform spiral lines and protrusions on the outer or inner surface of a solid. Generally, it has the following functions: tightening and connecting, suitable for the transmission function of most screw products at present: such as the micrometer used for QC inspection of dimensions; Sealing function: such as sealing the connection of pipelines.
To understand screws, one must first know their structure:
The screw is composed of a driving system, a head, a tooth joint, and an introduction and penetration part.
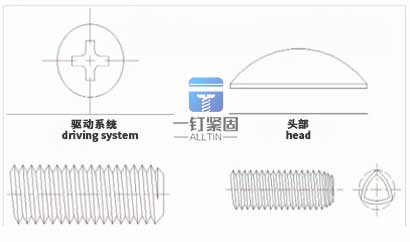
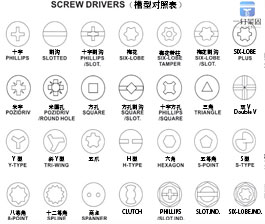
Most screw tooth types are generally divided into mechanical teeth and self tapping teeth.There are many classifications for head and groove shapes, each of which is different.The groove head shape can be combined with each other, so the screws have different shapes and functions.
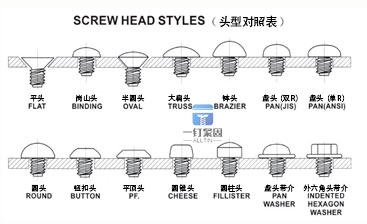
The thickness and diameter of the screw head can generally be customized. Usually, the head diameter is greater than 0.6mm on one side of the screw to cover the lock without piercing. If it is too small, it is easy to lock. For example, for M1.4 screws, the diameter of the screw head is 2.6mm. The opening diameter of the plastic screw hole is 1.6, and one side is covered with 0.5mm. With different product designs, screw specifications have increased and design parameters have also changed. For example, for M3.0 screws, the opening should exceed 3.5, so it is safe for the diameter of the screw head to exceed 5.0. This is just a simple list. Design parameters should be defined based on actual product design requirements. Nuts also need to consider the length and knurling depth of the nut in product design, which is related to whether the torque of the nut can meet the requirements.
The production standards for screws are divided into the following categories:
1.ANSI American National Standard (American Standard)
2.German National Standard (German Standard) ASME - American Society of Mechanical Engineers standard.
3.JIS - Japanese National Standard (Japanese Standard) BSW - British National Standard SO - International Standard.
4.GB National Standard is one of the numerous standards in China, including industry standards, professional standards, and some standards. National standards are divided into GB (mandatory standard), GB/T (recommended standard), and GBN (national internal standard). What we usually see is that GB30, GB5783, and other standards, apart from some basic dimensions such as head to face and head thickness, the most important difference in the above standards is the difference in the threaded part. GB. DIN.JIS and other threads are all MM (mm), collectively referred to as metric threads.
Fasteners can be seen everywhere in daily life, from house decoration to computers and mobile phones, screws and nuts can be seen at all times. If it is necessary to have a detailed understanding of the production process and surface treatment of screws, you can contact Alltin Fastener at any time.